Battery switch on travel trailer function is crucial for managing your RV’s power. Understanding how your battery switch works—whether it’s a single-pole, double-pole, or double-pole double-throw type—is key to safe and efficient power usage. This guide breaks down the different types, shows you how to connect and disconnect batteries safely, and helps you troubleshoot common problems. We’ll cover everything from preventing corrosion to integrating your battery switch with solar panels and inverters.
We’ll explore the inner workings of various battery switch types, offering clear diagrams and explanations of their advantages and disadvantages. Learn the best practices for maintaining your battery connections, preventing costly issues down the line. Plus, we’ll tackle troubleshooting, showing you how to diagnose problems and fix them yourself, saving you time and money.
Battery Switch Types in Travel Trailers
Choosing the right battery switch for your travel trailer is crucial for managing power and ensuring safety. Different switches offer varying levels of control and protection, impacting how you use your trailer’s batteries. Understanding the differences will help you select the best option for your needs.
Single-Pole Battery Switches
A single-pole switch is the simplest type. It’s essentially an on/off switch for a single battery. It allows you to disconnect the battery from the trailer’s electrical system completely, preventing parasitic drain and improving safety during maintenance or storage.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Switch Lever | Controls the connection/disconnection of the battery. |
| Input Terminal | Connects to the positive (+) terminal of the battery. |
| Output Terminal | Connects to the positive (+) terminal of the trailer’s electrical system. |
Advantages include simplicity and low cost. Disadvantages are its limited functionality; you can only connect or disconnect one battery at a time. It offers no way to switch between different battery banks.
Double-Pole Battery Switches
Double-pole switches offer a more significant safety advantage by isolating both the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the battery simultaneously. This completely breaks the circuit, providing better protection against accidental shorts or shocks during maintenance.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Switch Lever | Simultaneously controls both positive and negative connections. |
| Positive Input/Output Terminals | Connect to the positive (+) terminals of the battery and the trailer’s electrical system. |
| Negative Input/Output Terminals | Connect to the negative (-) terminals of the battery and the trailer’s electrical system. |
Advantages include improved safety due to simultaneous isolation of both terminals. The disadvantage remains limited functionality, similar to a single-pole switch, only capable of connecting or disconnecting one battery bank.
Double-Pole Double-Throw (DPDT) Battery Switches
A DPDT switch allows switching between two different battery banks (e.g., a house battery and a starting battery). This is very common in travel trailers with separate batteries for house power and engine starting. It provides flexibility to choose which battery bank powers the trailer’s systems.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Switch Lever | Selects between two different battery banks (position 1 and position 2). |
| Input Terminals (Bank 1 & Bank 2) | Connect to the positive (+) terminals of each battery bank. |
| Output Terminals | Connect to the positive (+) terminal of the trailer’s electrical system. Only one bank is connected at a time. |
| Negative Terminals (Bank 1 & Bank 2) | Connect to the negative (-) terminals of each battery bank. Both banks are usually connected simultaneously for the ground. |
Advantages include the ability to switch between multiple battery banks, providing flexibility in power management. Disadvantages include increased complexity and cost compared to simpler switches. Improper wiring can lead to issues.
Troubleshooting Common Battery Switch Issues
Your travel trailer’s battery switch is a crucial component, ensuring you have power when you need it. Problems with this switch can leave you stranded without lights, appliances, or even the ability to charge your batteries. Understanding common issues and how to troubleshoot them is essential for any RV owner.
Common Battery Switch Problems and Troubleshooting
A malfunctioning battery switch can manifest in several ways. Let’s explore some of the most frequent problems and how to address them.
- No Power: This is the most obvious sign of a problem. Check the fuses first, both in the switch itself and in your trailer’s main fuse box. A blown fuse indicates a short circuit somewhere in your system. Replace the fuse with one of the same amperage rating. If the fuse blows again immediately, you have a more serious electrical issue requiring professional attention.
If the fuses are fine, check the switch itself – is it properly engaged in the correct position? Try toggling it several times to ensure good contact. If no power still exists, examine the wiring for any loose connections or damage.
- Blown Fuses: Repeatedly blowing fuses indicates a short circuit somewhere in your electrical system. Before replacing the fuse, carefully inspect all wiring connected to the battery switch for any signs of damage, fraying, or exposed wires. Look for areas where wires might be rubbing against metal parts of the trailer. If you find damage, repair or replace the affected wiring before replacing the fuse.
So, you’re planning a trip? Awesome! Don’t forget travel insurance! Check out aon travel insurance for comprehensive coverage. They’ve got options for everything from lost luggage to medical emergencies. Speaking of medical, another great resource for travel insurance is aon travel insurance , which often offers competitive rates and excellent customer service. Seriously, getting insured is a smart move before you jet off; it gives you peace of mind and protects your investment.
If the fuse continues to blow, you’ll likely need professional electrical help to locate the short circuit.
- Faulty Switch: If the fuses are fine and you still have no power, the switch itself might be faulty. This could be due to corrosion, worn-out internal components, or simple mechanical failure. A visual inspection may reveal signs of corrosion or damage. If the switch appears damaged, it should be replaced. Ensure the replacement switch is compatible with your trailer’s electrical system.
Diagnosing a Malfunctioning Battery Switch with a Multimeter
A multimeter is an invaluable tool for diagnosing electrical problems. Using a multimeter, you can test the battery switch for continuity and voltage.
To test for continuity (whether the circuit is complete):
- Turn the battery switch OFF.
- Set your multimeter to the continuity setting (usually symbolized by a diode or a wave).
- Touch the multimeter probes to the terminals on either side of the switch.
- If the multimeter beeps and displays a low resistance reading (near zero ohms), the switch is closed, even though it’s supposed to be off. This indicates a faulty switch.
- Repeat the test with the switch in the ON position. You should get a similar result.
To test for voltage:
- Set your multimeter to the DC voltage setting (usually symbolized by a V with a — next to it).
- Turn the battery switch ON.
- Touch one probe to the positive terminal of the battery and the other to the positive terminal of the switch.
- You should read a voltage close to the battery’s voltage (e.g., 12V for a 12V system). A significantly lower reading or no reading indicates a problem with the wiring or the switch itself.
- Repeat this process for the negative terminals.
Remember to always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on any electrical components in your travel trailer to prevent accidental short circuits and shocks.
Battery Switch and Power Management Systems: Battery Switch On Travel Trailer Function
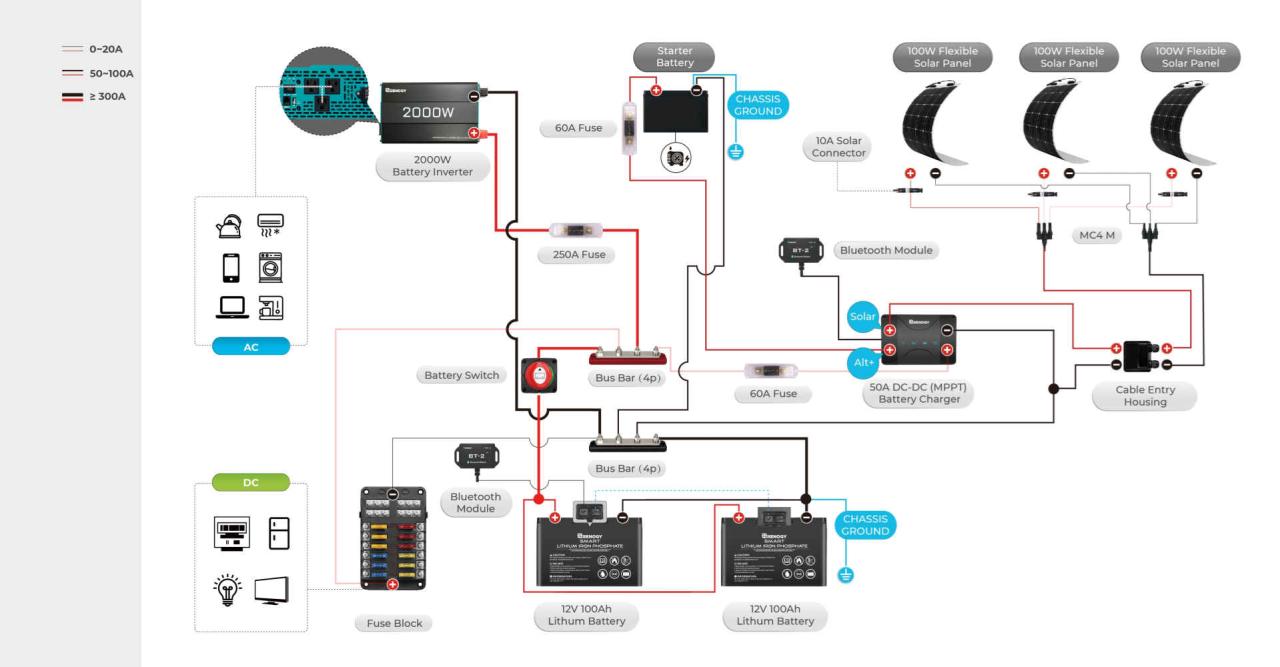
Your travel trailer’s battery switch is a crucial component, but it doesn’t operate in isolation. It’s a key player in a larger power management system, interacting with other elements to ensure efficient and safe power distribution. Understanding these interactions is vital for maximizing your RV’s power capabilities and preventing issues.The battery switch acts as the central on/off point for your house batteries.
So, you’re planning a trip? Awesome! Before you jet off, remember travel insurance is key. Check out Aon travel insurance for comprehensive coverage. They offer various plans, so find one that fits your needs and budget. Then, once you’ve got that sorted, consider looking at Aon travel insurance too – sometimes different providers offer slightly different perks, so comparing is a smart move.
Happy travels!
However, the flow of power doesn’t stop there. Solar panels, inverters, and converters all play a part, and their interaction with the battery switch dictates how power is sourced, stored, and used within your RV. For instance, with the switch “on,” solar panels can charge your batteries, while the inverter can draw power from them to run AC appliances.
With the switch “off,” the house batteries are disconnected from the rest of the system, preventing accidental drain.
Battery Switch Interconnections
The following table illustrates a simplified diagram of how the battery switch interacts with common power management components in a typical travel trailer. Remember, specific configurations can vary greatly depending on the RV’s make and model and any upgrades you’ve installed.
| Component | Function | Interaction with Battery Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Panels | Generate DC power from sunlight. | Connected to the battery charging system; the battery switch controls whether the charged power is available to the house system. When the switch is “off,” solar charging continues but the power is isolated from the house circuits. |
| Charge Controller | Regulates the charging current from solar panels to the batteries. | Usually placed between the solar panels and the batteries; its operation is independent of the battery switch, but the switch controls access to the charged batteries. |
| Batteries | Store DC power. | The battery switch is the primary on/off control for the house batteries, directly impacting their availability to other systems. |
| Converter | Converts 12V DC power from the batteries to 120V AC power for some appliances. | Draws power from the batteries; the battery switch controls whether this power is available. |
| Inverter | Converts 12V DC power from the batteries to 120V AC power for higher-power appliances. | Draws power from the batteries; the battery switch controls whether this power is available. |
| Shore Power Inlet | Provides AC power from an external source (campground hookup). | Usually charges the batteries through a converter/charger; the battery switch doesn’t directly control shore power but affects the availability of battery power when shore power is unavailable. |
Power Management System Configurations
Different RVs utilize various power management system setups. Some might use a simple system with only a battery switch and a basic converter, while others incorporate sophisticated systems with multiple charging sources, automatic switching, and monitoring capabilities. These configurations directly affect how the battery switch functions. For example, a system with an automatic charging relay will prioritize charging from shore power or solar before relying on the generator, even with the battery switch “on.” Conversely, a simpler system might rely solely on the battery switch to control power flow.
The impact on the battery switch’s role is that it becomes more of a simple on/off switch in simpler systems, while in more complex systems, it functions as one component within a larger, more automated control system.
Safety Considerations with Battery Switches
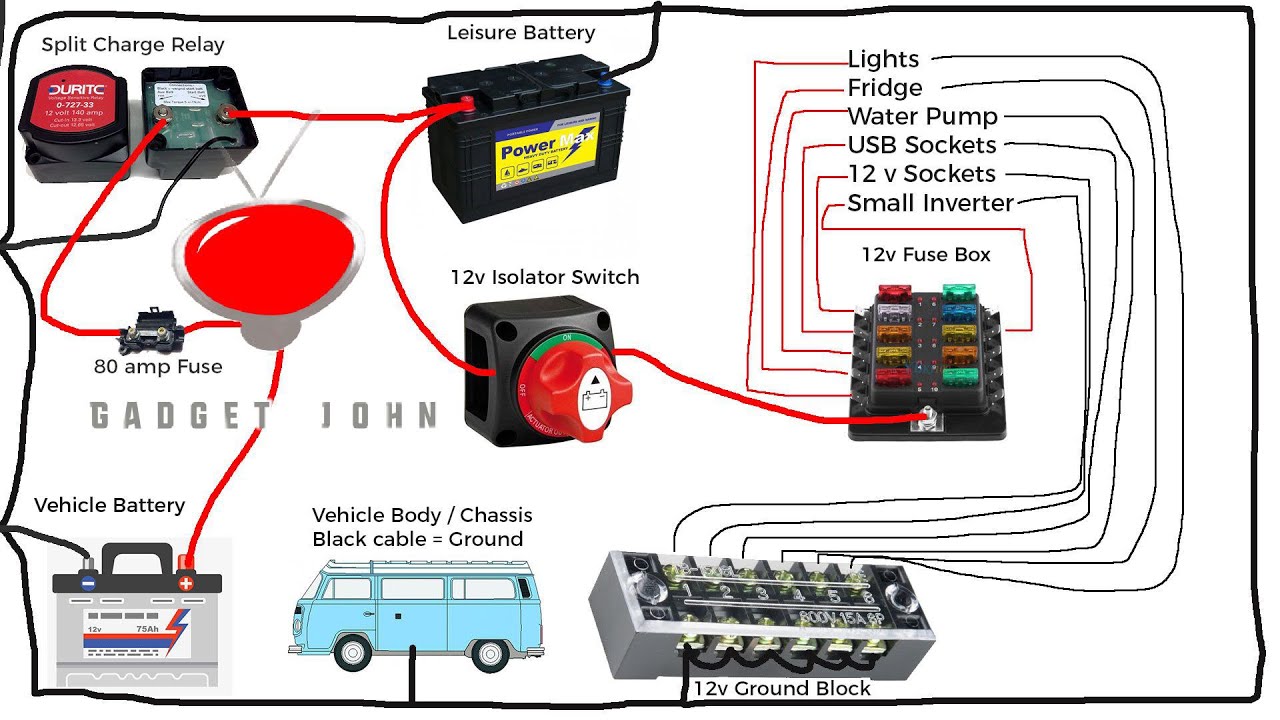
Working with batteries and electrical systems in your travel trailer requires careful attention to safety. Improper handling can lead to serious consequences, including electrical shock, burns, explosions, and even fire. Understanding the risks and following safe procedures is crucial for protecting yourself and your RV.Improper use or maintenance of a battery switch presents several potential hazards. Direct contact with battery terminals can result in a painful electrical shock, potentially leading to more severe injuries.
Loose connections or damaged wiring can create sparks, igniting flammable materials near the battery, such as spilled electrolyte or nearby propane tanks. Overloading the battery system can cause overheating and potentially lead to a fire. Furthermore, the release of hydrogen gas during battery charging presents an explosion risk if not properly ventilated.
Safe Handling Procedures for Batteries and Battery Switches, Battery switch on travel trailer function
Safe handling of batteries and switches is paramount. These procedures minimize the risk of accidents and ensure the longevity of your battery system.
- Always wear appropriate safety gear, including safety glasses and gloves, when working with batteries or the battery switch.
- Ensure adequate ventilation to prevent the buildup of flammable hydrogen gas, particularly during charging.
- Never allow metal tools or jewelry to come into contact with battery terminals to prevent short circuits.
- Before working on the battery system, disconnect the negative (-) terminal first, and reconnect it last. This prevents accidental short circuits.
- Inspect battery terminals and connections regularly for corrosion or damage. Clean terminals with a wire brush and baking soda solution if necessary.
- Use only approved battery chargers and maintain them according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Never mix different battery types (e.g., lead-acid and lithium-ion) in the same system unless specifically designed for compatibility.
- Keep the battery area clean and free of flammable materials.
- If you smell burning, smoke, or hear unusual noises from the battery system, immediately disconnect the battery switch and seek professional assistance.
Safety Guidelines for Working with Travel Trailer Battery Systems
Following these guidelines helps maintain a safe environment when working with your travel trailer’s battery system.
- Always turn off the battery switch before performing any maintenance or repairs on the battery system.
- Never work on the battery system while it’s raining or in damp conditions.
- Familiarize yourself with the location of your RV’s battery cutoff switch and know how to use it in case of emergency.
- Use a multimeter to check battery voltage and ensure proper charging.
- Regularly inspect all wiring and connections for signs of damage or corrosion.
- If you’re not comfortable working with electrical systems, consult a qualified RV technician.
- Properly dispose of old or damaged batteries according to local regulations.
Battery Switch Maintenance and Replacement
Keeping your travel trailer’s battery switch in top condition is crucial for reliable power and preventing costly repairs down the line. Regular maintenance ensures smooth operation and extends the lifespan of the switch and associated components, ultimately saving you time and money. Neglecting maintenance can lead to corrosion, faulty connections, and even complete switch failure, leaving you stranded without power.Regular maintenance and timely replacement of a faulty battery switch are key to maintaining reliable power in your travel trailer.
This section Artikels a maintenance schedule and provides a step-by-step guide for replacing the switch. Choosing the correct replacement is also discussed to ensure compatibility with your existing system.
Battery Switch Maintenance Schedule
A preventative maintenance schedule helps avoid unexpected problems. A simple visual inspection and cleaning should be part of your regular pre-trip checks. More thorough maintenance is recommended annually or every 12 months of use, whichever comes first.
- Monthly Inspection: Visually inspect the switch for any signs of corrosion, loose connections, or damage to the wiring. Tighten any loose connections and clean away any visible dirt or debris.
- Annual Maintenance: Disengage the battery switch. Use a wire brush and baking soda paste to clean the terminals and switch contacts thoroughly. Apply a dielectric grease to the terminals and connections to prevent corrosion. Check the wiring for any fraying or damage and replace if necessary.
Replacing a Faulty Battery Switch
Replacing a battery switch is a relatively straightforward process, but safety precautions should always be taken. Remember to always disconnect the battery’s negative terminal before starting any work on the electrical system.
- Gather Tools and Materials: You’ll need a screwdriver (likely Phillips head), wire cutters/strippers, a wire brush, dielectric grease, and a replacement battery switch of the same amperage and configuration as your old one. It’s also helpful to have a multimeter to test the connections before and after the replacement.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative (-) terminal of your battery. This is crucial for safety to prevent accidental shorts and shocks.
- Remove the Old Switch: Carefully disconnect the wires from the old battery switch. Take photos or make notes of how the wires are connected to aid in reinstallation. Use the appropriate screwdriver to remove the switch from its mounting location.
- Install the New Switch: Mount the new switch securely in the same location as the old one. Connect the wires to the new switch, ensuring they match the connections from the old switch (refer to your notes or photos). Double-check all connections for tightness and correct polarity.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative (-) terminal of your battery. Turn the switch to the “ON” position and check all your 12V systems to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Test the System: Use a multimeter to test the voltage at various points in your system to ensure proper power flow. This step verifies the new switch is working correctly and there are no short circuits.
Selecting a Compatible Replacement Battery Switch
Choosing the right replacement battery switch is vital for safety and proper operation. The new switch must match the amperage rating of your existing system and be appropriately sized for your battery bank.The amperage rating of the switch should be equal to or greater than the amperage rating of your battery bank. For example, if you have a 100-amp hour battery bank, a 100-amp or higher rated switch would be appropriate.
If unsure, consult the specifications of your original switch or contact a qualified RV technician. Also, consider the physical size and mounting style to ensure a proper fit.
Different Battery Switch Configurations and Their Applications
Choosing the right battery switch configuration for your travel trailer depends heavily on your power needs and the complexity of your electrical system. A simple setup might suffice for a smaller trailer with minimal appliances, while a more sophisticated system is necessary for larger trailers with numerous high-draw devices. Understanding the different configurations available will help you make an informed decision that ensures reliable power and protects your investment.
Different battery switch configurations offer varying levels of control and isolation for your house batteries and potentially your starting battery. The choice impacts how you manage power distribution, especially for high-demand appliances like air conditioners or microwaves. Proper configuration is crucial for preventing battery drain and ensuring consistent power to your appliances.
Battery Switch Configuration Comparison
The following table compares common battery switch configurations and their suitability for various travel trailers and power demands. Consider your trailer’s size, appliance usage, and desired level of control when making your selection.
| Configuration | Description | Suitable for | High-Draw Appliance Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Battery Switch | A single switch controls both house batteries. | Small trailers with low power demands. | May struggle with high-draw appliances; can lead to rapid battery drain if not carefully managed. |
| Dual Battery Switch | Separate switches control each house battery, allowing for independent control and monitoring. | Medium-sized trailers with moderate power demands. Offers better control than a single switch. | Allows for more efficient power management; high-draw appliances can be powered from one battery while the other charges. |
| Combination Battery Switch and Isolator | Combines a battery switch with an isolator to allow charging of house batteries while driving, even with the house batteries switched off. | Larger trailers with significant power demands; provides greater flexibility and safety. | Provides reliable power for high-draw appliances while charging, preventing premature battery drain. |
| Complex Multi-Bank Systems | More advanced systems that manage multiple battery banks (e.g., lithium and lead-acid) and offer sophisticated power distribution and monitoring capabilities. | Large luxury trailers with extensive electrical systems and high power demands. Often incorporates digital monitoring and control. | Efficiently handles high-draw appliances by distributing load and preventing overloads. |
Implications of Different Configurations for Load Types
High-draw appliances, such as air conditioners and microwaves, place significant strain on your battery system. The chosen battery switch configuration directly impacts how well the system manages this demand. A simple single switch may lead to rapid battery drain if a high-draw appliance is used for an extended period. More complex configurations, such as those with isolators and multiple switches, provide better control and prevent premature battery drain by allowing selective use of battery banks and charging while driving.
The Role of Battery Isolators
Battery isolators are crucial components that work in conjunction with battery switches. Their primary function is to prevent the house batteries from draining the vehicle’s starting battery. They allow the alternator to charge both the house and starting batteries simultaneously while driving, but they also isolate the batteries when the vehicle is off, preventing a dead starting battery.
Isolators typically use diodes or relays to manage power flow. They are often integrated into more complex battery switch systems to provide a more robust and efficient power management solution. A common example is a combination system that includes both a battery switch and an isolator, providing both selective control and charging capabilities.
Mastering your travel trailer’s battery switch is a game-changer for RVing. By understanding the different types, safe operating procedures, and common troubleshooting techniques, you’ll ensure reliable power and avoid potential hazards. Remember, regular maintenance and safe handling are paramount. So, confidently manage your power, extend the life of your battery system, and enjoy worry-free adventures on the road!
FAQ
What happens if I accidentally leave my battery switch on while storing my trailer?
Leaving the switch on can drain your batteries, potentially damaging them. Always turn it off when storing your trailer for extended periods.
How often should I check my battery switch connections?
Inspect your connections at least every three months, looking for corrosion or loose wires. More frequent checks are recommended in humid climates.
Can I use a multimeter to test my battery switch?
Yes, a multimeter can help you test for voltage drops across the switch and determine if it’s functioning correctly. There are online resources demonstrating how to do this safely.
What size breaker should I use with my battery switch?
The appropriate breaker size depends on the amperage of your battery system. Consult your trailer’s wiring diagram or a qualified electrician for the correct size.